For this calendar quarter, the NBA Coaches Association’s focus is on Heart Health and specifically on the importance of maintaining proper blood pressure levels. Part I of the Heart Health Bulletin takes the form of an education on hypertension (HTN) and how it is treated. Part II of the Heart Health Bulletin (February 2017) will take the form of the role that good nutrition can play in combating HTN and overall heart health.
*Hypertension (HTN) – TOP 5 FACTS
- 1 in 3 American adults have it, most common condition seen in primary care setting
- Only 50% of Americans have their Blood Pressure under control
- Often hypertension has no warning signs or symptoms…many individuals don’t know they have it!
- Hypertension often leads to heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, and death if not detected early and treated appropriately…Hypertension is commonly referred to as the ”silent killer.”
- Hypertension can be prevented.
HTN – WHAT IS IT?
- Blood pressure is the force of blood against your blood vessel walls as it circulates through your body.
- Blood pressure normally rises and falls throughout the day, but it can damage and weaken your arteries if it stays at a high level for a long time.
- Having high blood pressure raises your risk for heart disease and stroke, the leading causes of death in the United States.
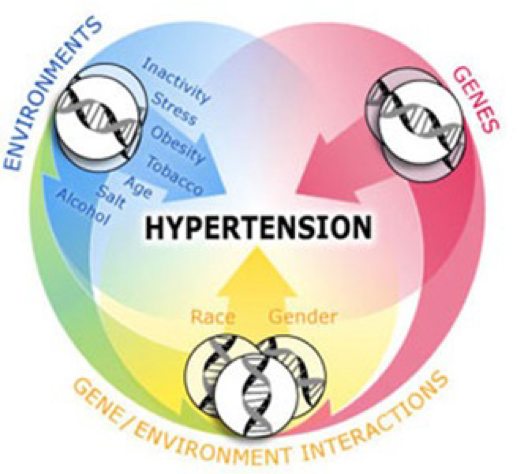
HTN – WHO GETS IT?
- Factors affecting blood pressure are strongly tied to lifestyle, ie; activity level, overweight/obesity, diet, smoking, alcohol use, social networks, sleep apnea, and stress.
- Hypertension tends to run in families (race, gender, cultural habits). Especially prevalent in African American males.
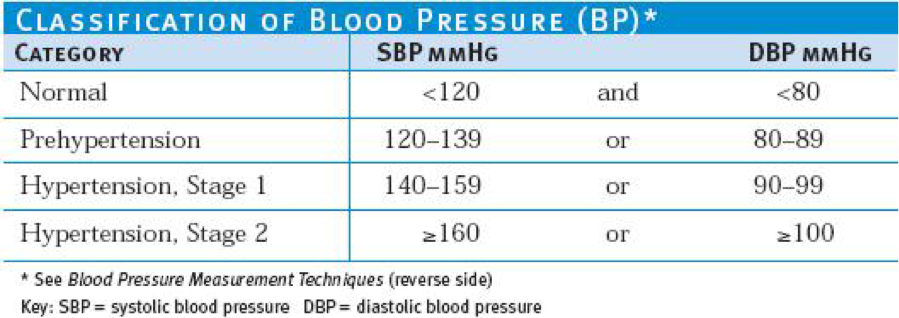
HTN – HOW IS IT DIAGNOSED?
- Usually requires three separate MD visits with elevated BP measurements.
HTN – HOW IS IT TREATED?
- The most effective treatment is healthy lifestyle changes…balance self-indulgence with self-awareness.
- Medications are often prescribed after an unsuccessful trial of lifestyle modifications.
HTN – TOP 5 TIPS TO IMPROVE BLOOD PRESSURE
- Proper sleep hygiene – Avoid large meals and stimulants such as caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol too close to bedtime. Exercise can promote good sleep. Ensure adequate exposure to natural light. Associate your bed with sleep. It is not a good idea to use your bed to watch TV, listen to the radio, or read. Make sure that the sleep environment is pleasant and relaxing.
- Exercise – But how much? The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends you get at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise, 75 minutes of vigorous exercise or a combination of both each week.
Moderate intensity
- Walking briskly (3 miles per hour or faster, but not race walking)
- Water aerobics
- Bicycling slower than 10 miles per hour
- Tennis (doubles)
- Ballroom dancing
- General gardening
Vigorous Intensity
Race walking, jogging, or running
Swimming laps
Tennis (singles)
Aerobic dancing
Bicycling 10 miles per hour or faster
Jumping rope
Heavy gardening (continuous digging or hoeing)
Hiking uphill or with a heavy backpack
Bottom Line – Regular exercise (vigorous) when possible will push that pressure down. More on Heart Health in the February 2017 Bulletin.